1. What is an anechoic chamber?
An anechoic chamber is a special testing environment designed to absorb electromagnetic or sound waves. Besides, it also prevents external waves from entering the chamber. Hence the results that you get simulates an empty infinite large room.
An American Acoustics formulated the term while he was referring to the acoustic anechoic chamber. But the term has recently been tuned to RF anechoic chambers. This can eliminate external noise and reflection caused by electromagnetic waves. There are many different types of anechoic chambers; some are small and compact table top sized enclosure, and some others are big as room sized or building sized.
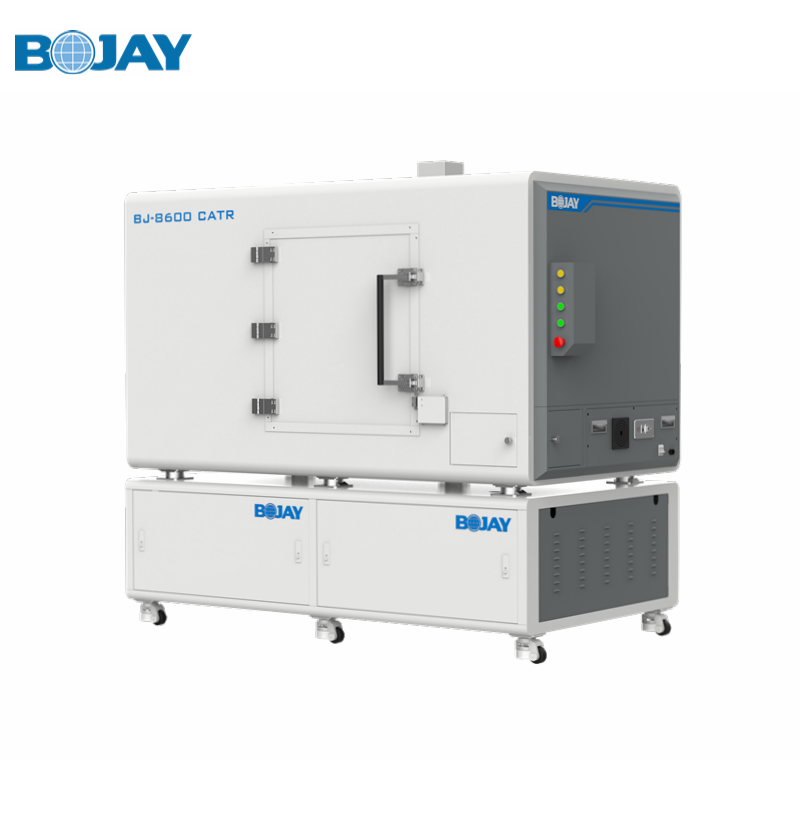

2. How does a RF anechoic chamber works?
To shield the external waves from entering the chamber, the walls of the RF chamber is designed with metallic or highly conductive material to work as Faraday cage.
The interior walls of the chamber are covered with radiation absorbent material. Rather than acoustically absorbent material as compared to an acoustic anechoic chamber. Therefore, the chamber eliminates external RF noise interference and internal reflection signals to enable an ideal environment for testing radars and antennas.
RF chambers are mostly used to ensure that the products comply with industry standards. However, others use it for radiated immunity testing, specific absorption rate testing, radiated emissions testing, and wireless transmitter testing.
The chamber houses the antennas while you take measurements of electromagnetic interference and antenna radiation patterns to ensure the performance meet the design expectations such as efficiency, gain, and pattern characteristics. An RF anechoic chamber ensures the evaluation of a complex device which incorporated GPS, RFID, WI-FI, Bluetooth, LTE, and MIMO can be done.
3. Features of an anechoic chamber
The interior radiation absorbent materials are crucial to the performance of the chamber. They are often pyramidal shape, but can be flat shape foam or ferrite tiles. The thickness of the absorber typically depends on frequency range of the applications and reflectivity attenuation requirement.
I/Os on the chamber are another feature that make the measurement possible. I/Os allow signals go in/out of the chamber to communicate with DUT or measurement equipment. All the ports need to maintain the isolation while passing required signals through, this could be challenging with increasing frequency expand into mmWave and extreme high data transfer rate,
Accurate and consistent positioning is the key for measurements, and this is also true for measurements inside an RF anechoic chamber. The positioner for DUT or measurement antenna need to have sufficient accuracy, resolution and repeatability to uncover possible issues and ensure pass yield on a production line.